Crack and Flaw Detection in Ceramics
Ceramic materials or ceramic composites are intensively used in various industries, such as automotive, electronics, aerospace, consumer, and defense to name a few. In general, most ceramics are hard, wear-resistant, refractory, thermal insulators, electrical insulators, nonmagnetic, oxidation resistant, prone to thermal shock, and chemically stable. Ceramics are harder and stiffer than steel; less dense (lighter) than most metals and metal alloys and their raw materials are both plentiful and inexpensive. In the mechanical sense, ceramics are hard but brittle. This is a direct consequence of covalent/ionic bonds between ceramic atoms. In practice, ceramic cracking is one of the fundamental problems that must be addressed by the industry.
Ultrasonic Technologies offers advanced diagnostics of ceramic material integrity using the proprietary Resonance Ultrasonic Vibrations (RUV) technology and tools. Three specific cases are presented below by (a) solid oxide fuel cells, (b) body armor plates, and (c) zirconia oxide dental discs.
(a) Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
Micro-cracks in fuel cells are either introduced from incoming substrates or created during various production steps, ultimately leading to product breakage and module cost increase. Cost reduction is a primary goal for new energy products to be competitive with fossil sources.
Ultrasonic Technologies, Inc. developed a new instrument for high volume in-line micro-crack inspection based on a novel methodology for advanced crack detection which includes the Resonance Ultrasonic Vibrations technique combined with the Activation Station (RUV-AS). Application of the RUV-AS system in fuel cell production dramatically increases production yield and reduces cost by screening out mechanically unstable ceramic plates caused by process flaws.
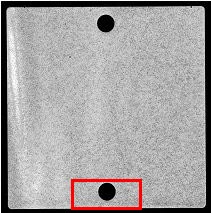
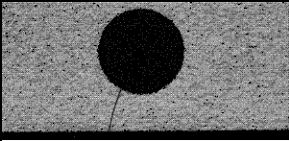
There are multiple locations in automatic production lines where RUV-AS equipment is a valuable cost-effective solution. These include testing of incoming ceramic substrates, processed wafers with deposited cathode/anode layers, and finished fuel cells. Importantly, all locations can be covered by a single device platform.


(b) Ceramic Armor Plates
Detection of Cracks and Delamination
The Resonance Ultrasonic Vibrations (RUV) technology was developed for non-destructive detection of cracks and delamination in composite ceramics used in body armor plates. The RUV technology implements fast measurement of the ultrasonic resonance response in ceramic substrates. Invisible peripheral or bulk cracks or delaminated components are exhibited as a deviation of the resonance response between the flawed plate and a standard plate. Also, the RUV tool allows “health” monitoring of the individual plate integrity during routine maintenance and rotation.
Ceramic substrates used to manufacture armor plates are the primary contributors to the overall performance of the finished product. Quality controls, concerning cracks and delamination, as well as process controls in production, are two primary aspects that require advanced testing efforts. To ensure that armor plates are not damaged and adhere to performance standards, periodic quality inspection is a mandatory requirement for armor plates employed in combat and special operations as well as after storage, shipping, and transportation. Commercially available the RUV-CP.1 model is used in plate production, while RUV-DBAM model is a deployable portable system (under development).
RUV technology provides:
1. Within seconds non-destructive inspection of mechanical flaws (cracks, delamination) during plate production
2. Detection of these mechanical flaws in fully assembled plates after deployment during periodic quality inspections in the field
3. Cost-effective solution to quality control and maintenance service.
Additionally, the RUV system serves as a process improvement tool that increases yield by eliminating production flaws caused by mechanical defects.
Frequency Curve
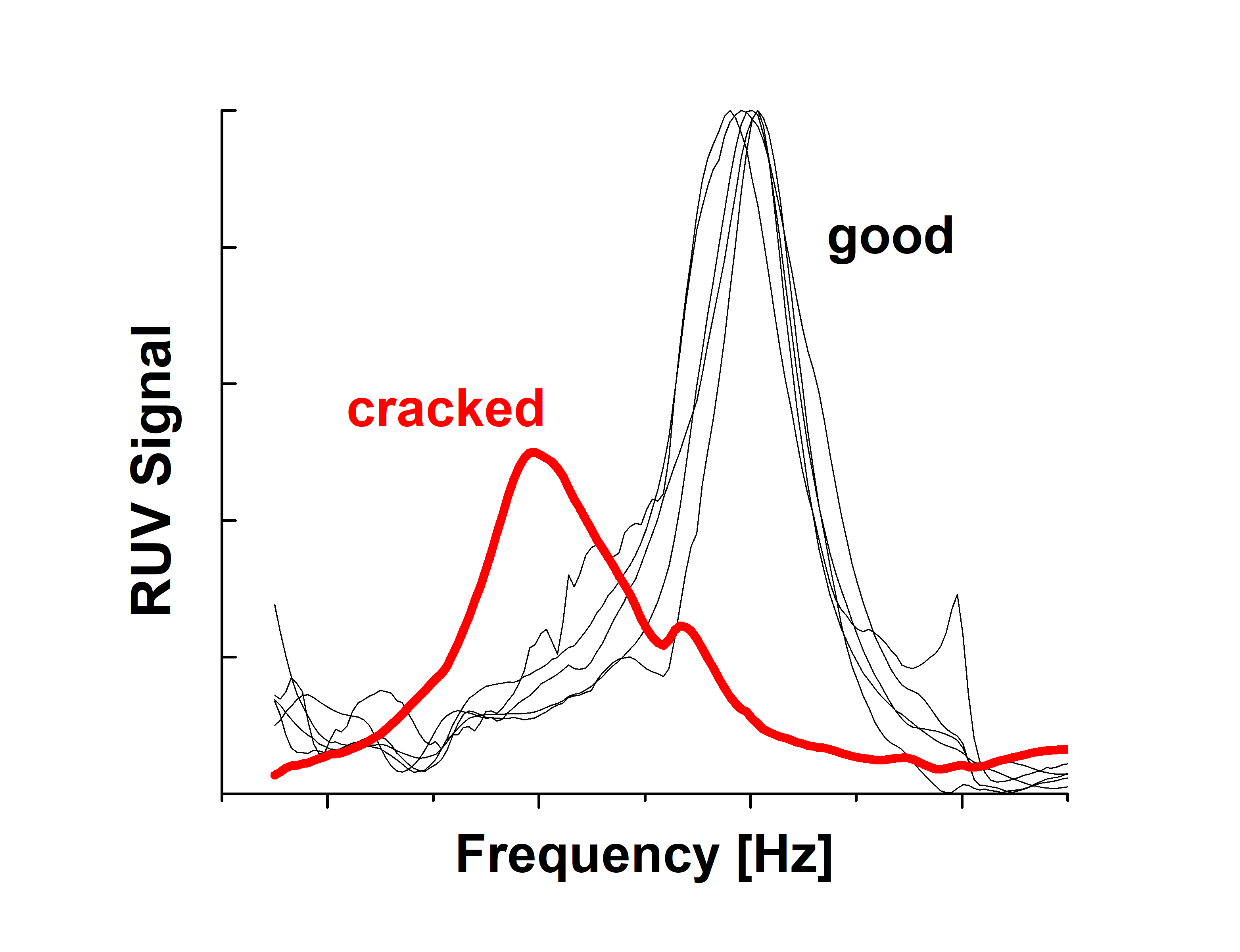
Through a resonance frequency curve selected from a broad range (20 - 250 kHz), the RUV method enables to detect both cracks and delamination in armor plates with simple quantitative criteria. A crack introduced into ceramic substrate alters RUV peak parameters: bandwidth and peak position. This is illustrated in Figure (left plot) by comparing RUV curves measured on four standard SAPI plates with the identical plate rejected due to internal crack. Specifically, the crack in the plate shows the following features: (1) a frequency shift of the peak position, and (2) an increase of the peak bandwidth.
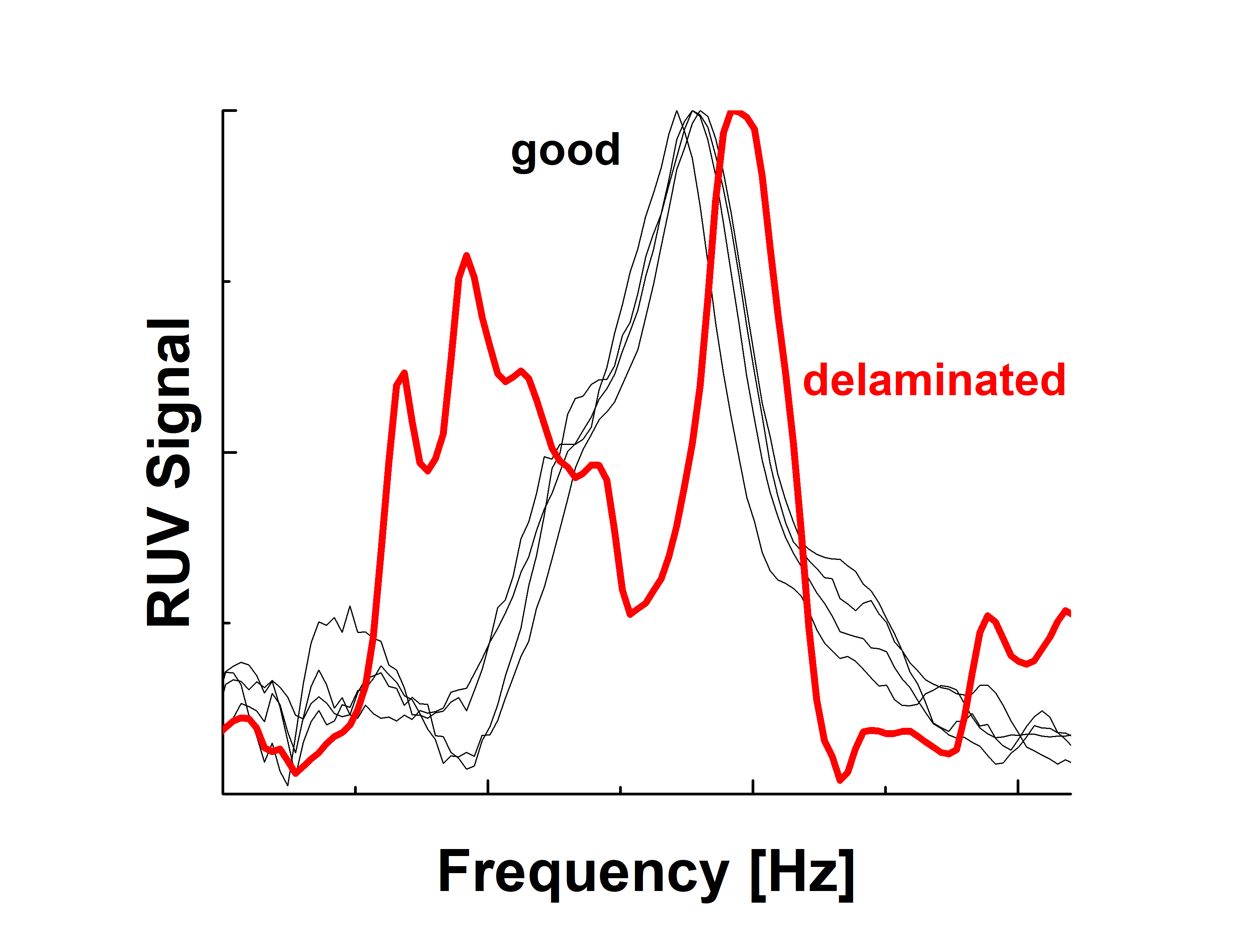
Delamination of armor plate components also alters RUV peak parameters: amplitude, bandwidth and peak position. This is illustrated in Figure (right plot) by comparing RUV curves measured on standard plates with the identical plate inspected by CT scan with confirmed delamination. Specifically, the delaminated plate shows a split of the primary broad peak on multiple sharp lines. This feature is automatically revealed by the RUV software. The RUV approach is based on fast measurement and analysis of a specific resonance peak and rejection of the suspect sample if peak characteristics deviate from similar non-cracked samples. Black lines in the plots represent good plates, the red line is a delaminated plate.
The RUV method to inspect delamination is based on a statistical approach. In case studies, the capture rate of the RUV method
approached 100%.
For more information, please contact us through the Ultrasonic Technologies website.
approached 100%.
For more information, please contact us through the Ultrasonic Technologies website.
(c) ZrO2 Dental Disc
FREQUENCY CURVE
Through a resonance frequency curve selected from a broad range (20 - 250 kHz), the Multi-Angle Vibrations (MAV) method enables screen out materials with hidden invisible cracks. A crack introduced into ceramics alters the MAV resonance peak. Specifically, the crack in the disc measured at different angles in the rotation mode shows large MAV peak variation between three scans compared to high coincidence for a good sample. The MAV approach is illustrated in Figures below.
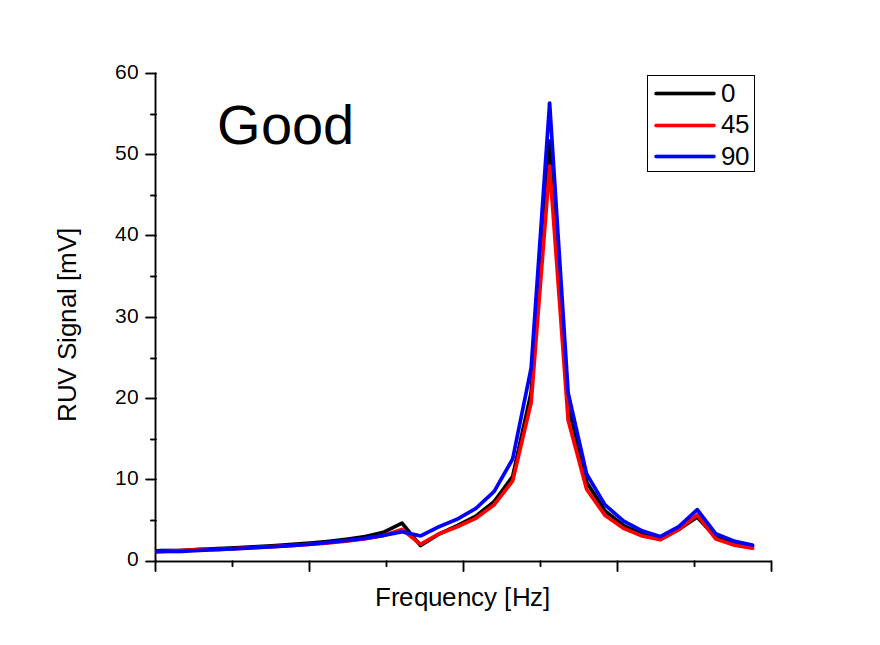
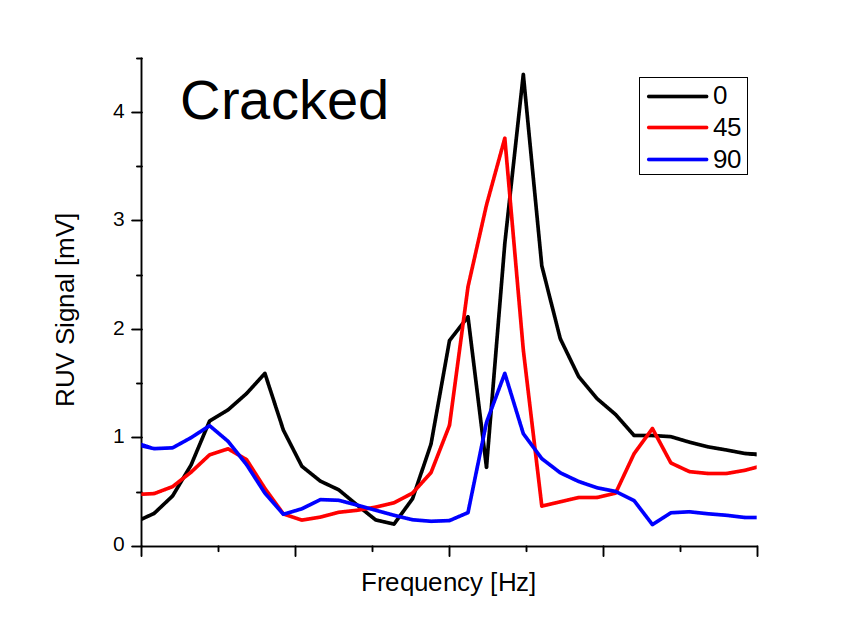
Therefore, the MAV method is based on a fast measurement and analyses (below 5 seconds per scan) of a specific resonance peak and automatic part rejection if peak characteristics deviate from the normal non-cracked samples. When used in ZrO2 disc production, the MAV system dramatically increases the yield and improves quality of dental products. Contact Ultrasonic Technologies at support@ultrasonictech.com to discuss details of MAV method.